Nawabs Of Bengal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of

 The Nawabs profited from the revenue generated by the worldwide demand of
The Nawabs profited from the revenue generated by the worldwide demand of 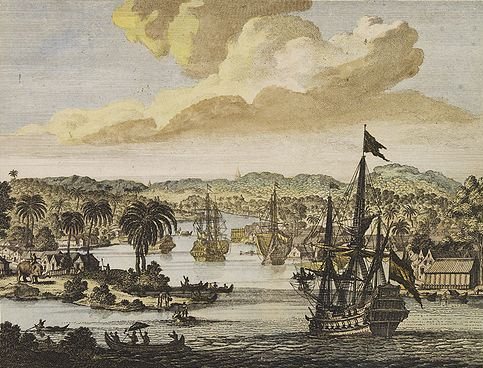 The Nawabs were patrons of
The Nawabs were patrons of  On 23 June 1757, the Battle of Plassey brought an end to the independence of the Nawabs of Bengal. Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah and his French allies were caught off guard by the defection of the Nawab's Commander-in-Chief Mir Jafar to the British side. The British, under the leadership of Robert Clive, gained enormous influence over Bengal Subah as a result of the battle. The last independent Nawab was arrested by his former officers and killed in revenge for the brutality against his courtiers.
On 23 June 1757, the Battle of Plassey brought an end to the independence of the Nawabs of Bengal. Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah and his French allies were caught off guard by the defection of the Nawab's Commander-in-Chief Mir Jafar to the British side. The British, under the leadership of Robert Clive, gained enormous influence over Bengal Subah as a result of the battle. The last independent Nawab was arrested by his former officers and killed in revenge for the brutality against his courtiers.
 Nawab Mansur Ali Khan was the last titular Nawab Nazim of Bengal. During his reign the ''nizamat'' at Murshidabad came to be debt-ridden. The Nawab left Murshidabad in February 1869, and had started living in England. The title of the Nawab of Bengal stood abolished in 1880. He returned to Bombay in October 1880 and pleaded his case against the orders of the government, but as it stood unresolved the Nawab renounced his styles and titles, abdicating in favour of his eldest son on 1 November 1880.
The
Nawab Mansur Ali Khan was the last titular Nawab Nazim of Bengal. During his reign the ''nizamat'' at Murshidabad came to be debt-ridden. The Nawab left Murshidabad in February 1869, and had started living in England. The title of the Nawab of Bengal stood abolished in 1880. He returned to Bombay in October 1880 and pleaded his case against the orders of the government, but as it stood unresolved the Nawab renounced his styles and titles, abdicating in favour of his eldest son on 1 November 1880.
The
The arrival of the Nawabs their decline
{{West Bengal Nawabs of Bengal Bengal Subah Indian nobility Noble titles created in 1717 1717 establishments in Asia Murshidabad district
Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Ben ...
in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
, and Orissa
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of Sch ...
which constitute the modern-day sovereign country of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
and the Indian state
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
s of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
and Orissa
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of Sch ...
. They are often referred to as the Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa ( bn, বাংলা, বিহার ও উড়িষ্যার নবাব). The Nawabs were based in Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
During ...
which was centrally located within Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha. Their chief, a former prime minister, became the first Nawab. The Nawabs continued to issue coins in the name of the Mughal Emperor, but for all practical purposes, the Nawabs governed as independent monarchs. Bengal continued to contribute the largest share of funds to the imperial treasury in Delhi. The Nawabs, backed by bankers such as the Jagat Seth
The Jagat Seth family was a wealthy merchant, banker and money lender family from Murshidabad in Bengal during the time of the Nawabs of Bengal.
History
The house was founded by Jain Hiranand Shah from Nagaur, Rajasthan, who came to Patna in ...
, became the financial backbone of the Mughal court. During the 18th century, the Nawabs of Bengal were among the wealthiest rulers in the world.William Dalrymple (10 September 2019). ''The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company''. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 308. .
The Nawabs of Bengal oversaw a period of proto-industrialization
Proto-industrialization is the regional development, alongside commercial agriculture, of rural handicraft production for external markets.
The term was introduced in the early 1970s by economic historians who argued that such developments in par ...
. The Bengal-Bihar-Orissa triangle was a major production center for cotton muslin cloth, silk cloth, shipbuilding, gunpowder, saltpetre, and metalworks. Factories were set up in Murshidabad, Dhaka, Patna, Sonargaon, Chittagong, Rajshahi, Cossimbazar, Balasore, Pipeli, and Hugli among other cities, towns, and ports. The region became a base for the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
, the French East India Company
The French East India Company (french: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a colonial commercial enterprise, founded on 1 September 1664 to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in the ...
, the Danish East India Company
The Danish East India Company ( da, Ostindisk Kompagni) refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-fo ...
, the Austrian East India Company
Austrian East India Company (german: Österreichische Ostindien-Kompanie) is a catchall term referring to a series of Austrian trading companies based in Ostend and Trieste. The Imperial Asiatic Company of Trieste and Antwerp (french: Société i ...
, the Ostend Company
The Ostend Company ( nl, Oostendse Compagnie, french: Compagnie d'Ostende), officially the General Company Established in the Austrian Netherlands for Commerce and Navigation in the Indies () was a chartered trading company in the Austrian Netherl ...
, and the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
.
The British company eventually rivaled the authority of the Nawabs. In the aftermath of the siege of Calcutta
The siege of Calcutta was a battle between the Nawab of Bengal and the Kingdom of Great Britain, British East India Company on 20 June 1756. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah, aimed to seize Calcutta to punish the company for the unauthoris ...
in 1756, in which the Nawab's forces overran the main British base, the East India Company dispatched a fleet led by Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
who defeated the last independent Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Be ...
at the Battle of Plassey in 1757. Mir Jafar was installed as the puppet Nawab. His successor Mir Qasim
Mir Qasim ( bn, মীর কাশিম; died 8 May 1777) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1760 to 1763. He was installed as Nawab with the support of the British East India Company, replacing Mir Jafar, his father-in-law, who had himself been su ...
attempted in vain to dislodge the British. The defeat of Nawab Mir Qasim of Bengal, Nawab Shuja-ud-Daula
Shuja-ud-Daula (b. – d. ) was the Subedar and Nawab of Oudh and the Vizier of Delhi from 5 October 1754 to 26 January 1775.
Early life
Shuja-ud-Daula was the son of the Mughal Grand Vizier Safdarjung chosen by Ahmad Shah Bahadur. Unlike ...
of Oudh
The Oudh State (, also Kingdom of Awadh, Kingdom of Oudh, or Awadh State) was a princely state in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the British in 1856. The name Oudh, now obsolete, was once the anglicized name of ...
, and Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
at the Battle of Buxar in 1764 paved the way for British expansion across India. The South Indian Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
led by Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He int ...
overtook the Nawab of Bengal as the subcontinent's wealthiest monarchy; but this was short-lived and ended with the Anglo-Mysore War
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Kingdom of Mysore#Under Haider Ali and Tipu Sultan, Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (r ...
. The British then turned their sights on defeating the Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
and Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
.
In 1772, Governor-General Warren Hastings shifted administrative and judicial offices from Murshidabad to Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
, the capital of the newly formed Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
, and the ''de facto'' capital of British India. The Nawabs had lost all independent authority since 1757. In 1858, the British government abolished the symbolic authority of the Mughal court. After 1880, the descendants of the Nawabs of Bengal were recognised simply as Nawabs of Murshidabad
The Nawab Bahadur of Murshidabad ( bn, মুর্শিদাবাদের নবাব বাহাদুর), or simply known as the Nawab of Murshidabad, was a hereditary title of Bengal akin to Western peerage. They were direct descenda ...
with the mere status of a peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Belgi ...
.
History

Independent nawabs
The Bengal Subah was the wealthiestsubah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''subed ...
of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. There were several posts under the Mughal administrative system of Bengal since Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
's conquest in the 1500s. ''Nizamat'' (governornership) and ''diwani'' (premiership) were the two main branches of provincial government under the Mughals. The '' Subahdar'' was in-charge of the ''nizamat'' and had a chain of subordinate officials on the executive side, including ''diwans'' (prime ministers) responsible for revenue and legal affairs. The regional decentralization of the Mughal Empire led to the creation of numerous semi-independent strongholds in the Mughal provinces. As the Mughal Empire began to decline, the Nawabs rose in power. By the early 1700s, the Nawabs were practically independent, despite a nominal tribute to the Mughal court.
The Mughal court heavily relied on Bengal for revenue. Azim-us-Shan
Azim-ush-Shan ( fa, ; 15 December 1664 – 18 March 1712) was the second son of Mughal emperor Shah Alam I, by his second wife, Amrita Bai, Princess of Kishangarh. He was the grandson of Emperor Aurangzeb, during whose reign, he was the '' s ...
, the Mughal viceroy of Bengal, had a bitter power struggle with his prime minister ('' diwan'') Murshid Quli Khan. Emperor Aurangzeb transferred Azim-us-Shan out of Bengal as a result of the disputes. After the viceroy's exit, the provincial premier Murshid Quli Khan emerged as the ''de facto'' ruler of Bengal. His administrative coup merged the offices of the ''diwan'' (prime minister) and ''subedar'' (viceroy). In 1716, Khan shifted Bengal's capital from Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
to a new city named after himself. In 1717, Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar recognized Khan as the hereditary Nawab Nazim. The Nawab's jurisdiction covered districts in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa. The Nawab's territory stretched from the border with Oudh
The Oudh State (, also Kingdom of Awadh, Kingdom of Oudh, or Awadh State) was a princely state in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the British in 1856. The name Oudh, now obsolete, was once the anglicized name of ...
in the west to the border with Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
in the east.
The chief deputy of the Nawab was the Naib Nazim of Dhaka, the mayor of the former provincial capital whose own wealth was considerable; the Naib Nazim of Dhaka also governed much of eastern Bengal. Other important officials were stationed in Patna, Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literall ...
, and Chittagong. The aristocracy was composed of the Zamindars of Bengal
The Zamindars of Bengal were zamindars (hereditary landlords) of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent (now divided between Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). They governed an ancient system of land ownership.
The Bengali ...
. The Nawab was backed up by the powerful Jagat Seth family of bankers and money lenders. The Jagat Seth controlled the flow of Bengali revenue into the imperial treasury in Delhi. They served as financiers to both the Nawabs and European companies operating in the region.
 The Nawabs profited from the revenue generated by the worldwide demand of
The Nawabs profited from the revenue generated by the worldwide demand of muslin trade in Bengal
Muslin, a cotton fabric of plain weave, was historically hand woven in the areas of Dhaka and Sonargaon in Bangladesh and exported for many centuries. The region forms the eastern part of the historic region of Bengal.
Origins
Bengal has manufa ...
, which was centered in Dhaka and Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
. Murshidabad was a major center of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
production. Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
in Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
enjoyed Ottoman and European demand. Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
was a center of metalworks and the military-industrial complex. The Bengal-Bihar region was a major exporter of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). ...
and saltpetre
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitra ...
. The Nawabs presided over an era of growing organization in banking, handicrafts
A handicraft, sometimes more precisely expressed as artisanal handicraft or handmade, is any of a wide variety of types of work where useful and decorative objects are made completely by one’s hand or by using only simple, non-automated re ...
, and other trades.
Bengal attracted traders from across Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
. Traders were lodged at caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering ...
s, including the Katra Masjid
The Katra Masjid is a former caravanserai, mosque and the tomb of Nawab Murshid Quli Khan. It was built between 1723 and 1724. It is one of the largest caravanserais in the Indian subcontinent. It was built during the 18th century, when the ear ...
in Murshidabad; and the Bara Katra
Bara Katra ( bn, বড় কাটরা; Great Caravanserai) is one of the oldest historical and architectural monuments in Dhaka. The word Katra may have originated from Arabic word Katara which means colonnaded building. 'Katra/ katara' in ...
and Choto Katra
Chhota Katra ( bn, ছোট কাটারা; ''Small Katra'') is one of two Katras built during Mughal's regime in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It was constructed in 1663 by Subahdar Shaista Khan. It is on Hakim Habibur Rahman lane on the bank of the B ...
in Dhaka. Dutch Bengal
Bengal was a directorate of the Dutch East India Company in Mughal Bengal between 1610 until the company's liquidation in 1800. It then became a colony of the Kingdom of the Netherlands until 1825, when it was relinquished to the British accor ...
i trading posts included the main Dutch port of Pipeli in Orissa; the Dutch settlement in Rajshahi
A trading post of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) existed in Rajshahi, Bengal, during the 18th century. The Dutch were the first Europeans to arrive in this area. The trading station was located on the banks of the Padma River. It included fa ...
; and the towns of Cossimbazar
Cossimbazar is a sub-urban area of Berhampore City in the Berhampore CD block in the Berhampore subdivision in Murshidabad district in the Indian state of West Bengal."Cossimbazar" in ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', Oxford, Clarendon Press, ...
and Hugli. The Danes built trading posts in Bankipur
Bankipur is a neighbourhood and residential area in Patna, in the Indian state of Bihar. It is located on the bank of the river Ganges. The prime attraction is the Khuda Bakhsh Oriental Library built by Khan Bahadur Khuda Bakhsh in 1891 and Gol ...
and on islands of the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
. Balasore
Balasore or Baleswara is a city in the state of Odisha, about north of the state capital Bhubaneswar and from Kolkata, in eastern India. It is the largest town of northern Odisha and the administrative headquarters of Balasore district. It i ...
in Orissa was a prominent Austrian trading post. Bengali cities were full of brokers, workers, peons, naibs, wakils, and ordinary traders.
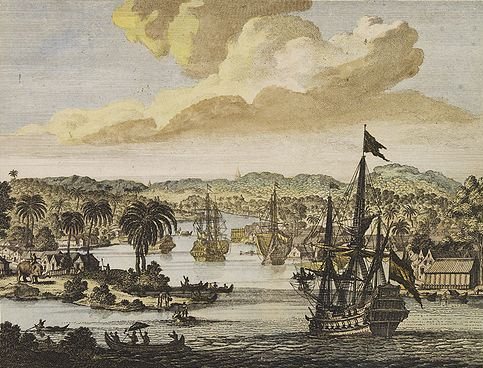 The Nawabs were patrons of
The Nawabs were patrons of the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
, including the Murshidabad style of Mughal painting
Mughal painting is a style of painting on paper confined to miniature (illuminated manuscript), miniatures either as book illustrations or as single works to be kept in albums (muraqqa), from the territory of the Mughal Empire in South Asia. It e ...
, Hindustani classical music
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of northern regions of the Indian subcontinent. It may also be called North Indian classical music or, in Hindustani, ''shastriya sangeet'' (). It is played in instruments like the violin, sita ...
, the Baul
The Baul ( bn, বাউল) are a group of mystic minstrels of mixed elements of Sufism, Vaishnavism and Tantra from Bangladesh and the neighboring Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley and Meghalaya. Bauls cons ...
tradition, and local craftsmanship. The second Nawab Shuja-ud-Din Muhammad Khan
Shuja-ud-Din Muhammad Khan ( bn, সুজাউদ্দীন মুহম্মদ খাঁন, fa, ) was the Nawab of Bengal. He married Zainab un-nisa Begum and Azmat un-nisa Begum, the daughters of Murshid Quli Khan by Nasiri Banu Beg ...
developed Murshidabad's royal palace, military base, city gates, revenue office, public audience hall (durbar
Durbar can refer to:
* Conference of Rulers, a council of Malay monarchs
* Durbar festival, a yearly festival in several towns of Nigeria
* Durbar floor plate, a hot-rolled structural steel that has been designed to give excellent slip resistance ...
), and mosques in an extensive compound called Farrabagh (Garden of Joy) which included canals, fountains, flowers, and fruit trees. The second Nawab's reign saw a period of economic and political consolidation.
The third Nawab Sarfaraz Khan
Sarfarāz Khān ( bn, সরফরাজ খান, fa, ; c. 1700 – 29 April 1740), born ''Mīrza Asadullāh'', was a Nawab of Bengal. Sarfaraz Khan's maternal grandfather, Nawab Murshid Quli Khan of Bengal (Bengal, Bihar and Orissa) nomin ...
was preoccupied with military engagements, including Nader Shah's invasion of India
Emperor Nader Shah, the Shah of Iran (1736–47) and the founder of the Afsharid dynasty, invaded Northern India, eventually attacking Delhi in March 1739. His army had easily defeated the Mughals at the Battle of Karnal and would eventually cap ...
. Sarfaraz Khan was killed at the Battle of Giria
The Battle of Giria were two battles that took place in Giria, India, Giria, an insignificant census town in Bengal, although not well known, were very significant in the history of Bengal and like the Battle of Plassey, had far reaching consequen ...
by his deputy Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan (1671 – 9 April 1756) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1740 to 1756. He toppled the Nasiri dynasty of Nawabs by defeating Sarfaraz Khan in 1740 and assumed power himself.
During much of his reign Alivardi encountered frequent Mar ...
. The coup by Alivardi Khan led to the creation of a new dynasty. Nawab Alivardi Khan endured brutal raids by the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
. The Marathas undertook six expeditions in Bengal from 1741–1748. The Maratha general Raghunath Rao
Raghunathrao Bhat (a.k.a. Ragho Ballal or Ragho Bharari) (18 August 1734 – 11 December 1783) was the 11th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire for a brief period from 1773 to 1774. He was known among the Hindus for his extremely successful North-west ...
conquered large parts of Orissa. Nawab Alivardi Khan made peace with Raghunathrao in 1751, ceding large parts of Orissa up to the river Subarnarekha. The Marathas demanded an annual tribute payment. The Marathas also promised to never to cross the boundary of the Nawab's territory. European trading companies also grew more influential in Bengal.
The Nawabs were also notorious for their repressive tactics, including torture for non-payment of land rent. Nawab Alivardi Khan's successor was Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Be ...
.Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah grew increasingly wary of the British presence in Bengal. He also feared invasions by the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
from the north and Marathas from the west. On 20 June 1756, Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah launched the siege of Calcutta
The siege of Calcutta was a battle between the Nawab of Bengal and the Kingdom of Great Britain, British East India Company on 20 June 1756. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah, aimed to seize Calcutta to punish the company for the unauthoris ...
, in which he won a decisive victory. The British were briefly expelled from Fort William, which came under the occupation of the Nawab's forces. The East India Company dispatched a naval fleet led by Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
to regain control of Fort William. By January 1757, the British retook Fort William. The stalemate with the Nawab continued into June. The Nawab also began cooperating with the French East India Company, raising the ire of the British further. Britain and France were at the time pitted against each other in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
.
 On 23 June 1757, the Battle of Plassey brought an end to the independence of the Nawabs of Bengal. Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah and his French allies were caught off guard by the defection of the Nawab's Commander-in-Chief Mir Jafar to the British side. The British, under the leadership of Robert Clive, gained enormous influence over Bengal Subah as a result of the battle. The last independent Nawab was arrested by his former officers and killed in revenge for the brutality against his courtiers.
On 23 June 1757, the Battle of Plassey brought an end to the independence of the Nawabs of Bengal. Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah and his French allies were caught off guard by the defection of the Nawab's Commander-in-Chief Mir Jafar to the British side. The British, under the leadership of Robert Clive, gained enormous influence over Bengal Subah as a result of the battle. The last independent Nawab was arrested by his former officers and killed in revenge for the brutality against his courtiers.
British influence and succession
Mir Jafar was installed as the puppet Nawab by the British. However, Jafar entered into a secret treaty with the Dutch East India Company. This caused the British to replace Mir Jafar with his son-in-lawMir Qasim
Mir Qasim ( bn, মীর কাশিম; died 8 May 1777) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1760 to 1763. He was installed as Nawab with the support of the British East India Company, replacing Mir Jafar, his father-in-law, who had himself been su ...
in October 1760. In one of his first acts, Mir Qasim ceded Chittagong, Burdwan
Bardhaman (, ) is a city and a municipality in the state of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of Purba Bardhaman district, having become a district capital during the period of British rule. Burdwan, an alternative name for the city, ...
and Midnapore
Medinipur or Midnapore (Pron: med̪iːniːpur) is a city known for its history in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the West Medinipur district. It is situated on the banks of the Kangsabati River (variously known as '' ...
to the East India Company. Mir Qasim also proved to be a popular ruler. But Mir Qasim's independent spirit eventually raised British suspicions. Mir Jafar was reinstalled as Nawab in 1763. Mir Qasim continued opposing the British and his father-in-law. He set up his capital in Munger
Munger, formerly spelt as Monghyr, is a twin city and a Municipal Corporation situated in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the administrative headquarters of Munger district and Munger Division. Munger was one of the major cities in Eastern In ...
and raised an independent army. Mir Qasim attacked British positions in Patna, overrunning the Company's offices and killing its Resident. Mir Qasim also attacked the British-allied Gorkha Kingdom
Gorkha Kingdom ( ne, गोरखा राज्य) was a member of the Chaubisi rajya, a confederation of 24 states on the Indian subcontinent ruled by Khas people. In 1743 CE, the kingdom began a campaign of military expansion, annexing se ...
. Mir Qasim allied with Nawab Shuja-ud-Daula
Shuja-ud-Daula (b. – d. ) was the Subedar and Nawab of Oudh and the Vizier of Delhi from 5 October 1754 to 26 January 1775.
Early life
Shuja-ud-Daula was the son of the Mughal Grand Vizier Safdarjung chosen by Ahmad Shah Bahadur. Unlike ...
of Awadh
Awadh (), known in British historical texts as Avadh or Oudh, is a region in the modern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, which was before independence known as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh. It is synonymous with the Kośāla region of ...
and Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
. However, the Mughal allies were defeated at the Battle of Buxar in 1764, which was the last real chance of resisting British expansion across the northern Indian subcontinent.
The South Indian Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
under Haider Ali and Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He int ...
briefly eclipsed the dominant position of Bengal in the subcontinent. Tipu Sultan pursued aggressive military modernization; and set up a company to trade with communities around the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea. Mysore's military technology at one point rivaled European technology. However, the Anglo-Mysore War
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Kingdom of Mysore#Under Haider Ali and Tipu Sultan, Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (r ...
ended Tipu Sultan's ascendancy.William Dalrymple (10 September 2019). The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company. Bloomsbury Publishing. .
In 1765, Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
became the first Governor of Bengal. He secured for the Company the ''diwani'' of the Bengal subah in perpetuity, from the Mughal emperor Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
. With this the system of dual governance was established and the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
was formed. In 1772, this arrangement came to be abolished and Bengal was brought under direct control of the British. In 1793, when the ''nizamat'' of the Nawab was also taken away they remained as the mere pensioners of the Company. After the Revolt of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the fo ...
, Company rule in India ended, and the British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
, in 1858, took over the territories which were under direct rule of the Company. This marked the beginning of the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
, and the Nawabs had no political or any other kind of control over the territory. Mir Jafar's descendants continued to live in Murshidabad. The Hazarduari Palace
Hazarduari Palace, earlier known as the ''Bara Kothi'', is located in the campus of Kila Nizamat in Murshidabad, in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is situated near the bank of river Ganges. It was built in the nineteenth century by archit ...
(''Palace of a Thousand Doors'') was built as the residence of the Nawabs in the 1830s. The palace was also used by British colonial officials.
 Nawab Mansur Ali Khan was the last titular Nawab Nazim of Bengal. During his reign the ''nizamat'' at Murshidabad came to be debt-ridden. The Nawab left Murshidabad in February 1869, and had started living in England. The title of the Nawab of Bengal stood abolished in 1880. He returned to Bombay in October 1880 and pleaded his case against the orders of the government, but as it stood unresolved the Nawab renounced his styles and titles, abdicating in favour of his eldest son on 1 November 1880.
The
Nawab Mansur Ali Khan was the last titular Nawab Nazim of Bengal. During his reign the ''nizamat'' at Murshidabad came to be debt-ridden. The Nawab left Murshidabad in February 1869, and had started living in England. The title of the Nawab of Bengal stood abolished in 1880. He returned to Bombay in October 1880 and pleaded his case against the orders of the government, but as it stood unresolved the Nawab renounced his styles and titles, abdicating in favour of his eldest son on 1 November 1880.
The Nawabs of Murshidabad
The Nawab Bahadur of Murshidabad ( bn, মুর্শিদাবাদের নবাব বাহাদুর), or simply known as the Nawab of Murshidabad, was a hereditary title of Bengal akin to Western peerage. They were direct descenda ...
succeeded the Nawab Nazims following Nawab Mansur Ali Khan's abdication, The Nawab Bahadurs had ceased to exercise any significant power. but were relegated to the status of a zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as a ...
and continued to be a wealthy family, producing bureaucrats and army officers.
List of Nawabs
The following is a list of the Nawabs of Bengal. Sarfaraz Khan and Mir Jafar were the only two to become Nawab Nazim twice. The chronology started in 1717 with Murshid Quli Khan and ended in 1880 with Mansur Ali Khan.Nawabs of Bengal under Mughal suzerainty
Nawabs of Bengal under British rule
References
External links
The arrival of the Nawabs their decline
{{West Bengal Nawabs of Bengal Bengal Subah Indian nobility Noble titles created in 1717 1717 establishments in Asia Murshidabad district